Stress is inevitable. But too much of it can be terrible for our health. Chronic stress can increase our risk for heart disease and strokes. It may also help cancer spread. How this works has remained a mystery—a challenge for cancer care. Xue-Yan He, a former postdoc in Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Adjunct Professor Mikala Egeblad’s lab, explains:
“Stress is something we cannot really avoid in cancer patients. You can imagine if you are diagnosed, you cannot stop thinking about the disease or insurance or family. So it is very important to understand how stress works on us.”
Now, He and Egeblad may have reached a breakthrough in understanding exactly that. Working with CSHL Professors Linda Van Aelst, David Spector, and Christopher Vakoc, they discovered that stress causes certain white blood cells called neutrophils to form sticky web-like structures that make body tissues more susceptible to metastasis. The finding could point to new treatment strategies that stop cancer’s spread before it starts.
The team arrived at their discovery by mimicking chronic stress in mice with cancer. They first removed tumors that had been growing in mice’s breasts and spreading cancer cells to their lungs. Next, they exposed the mice to stress. What He observed was shocking. Egeblad recalls:
“She saw this scary increase in metastatic lesions in these animals. It was up to a fourfold increase in metastasis.”
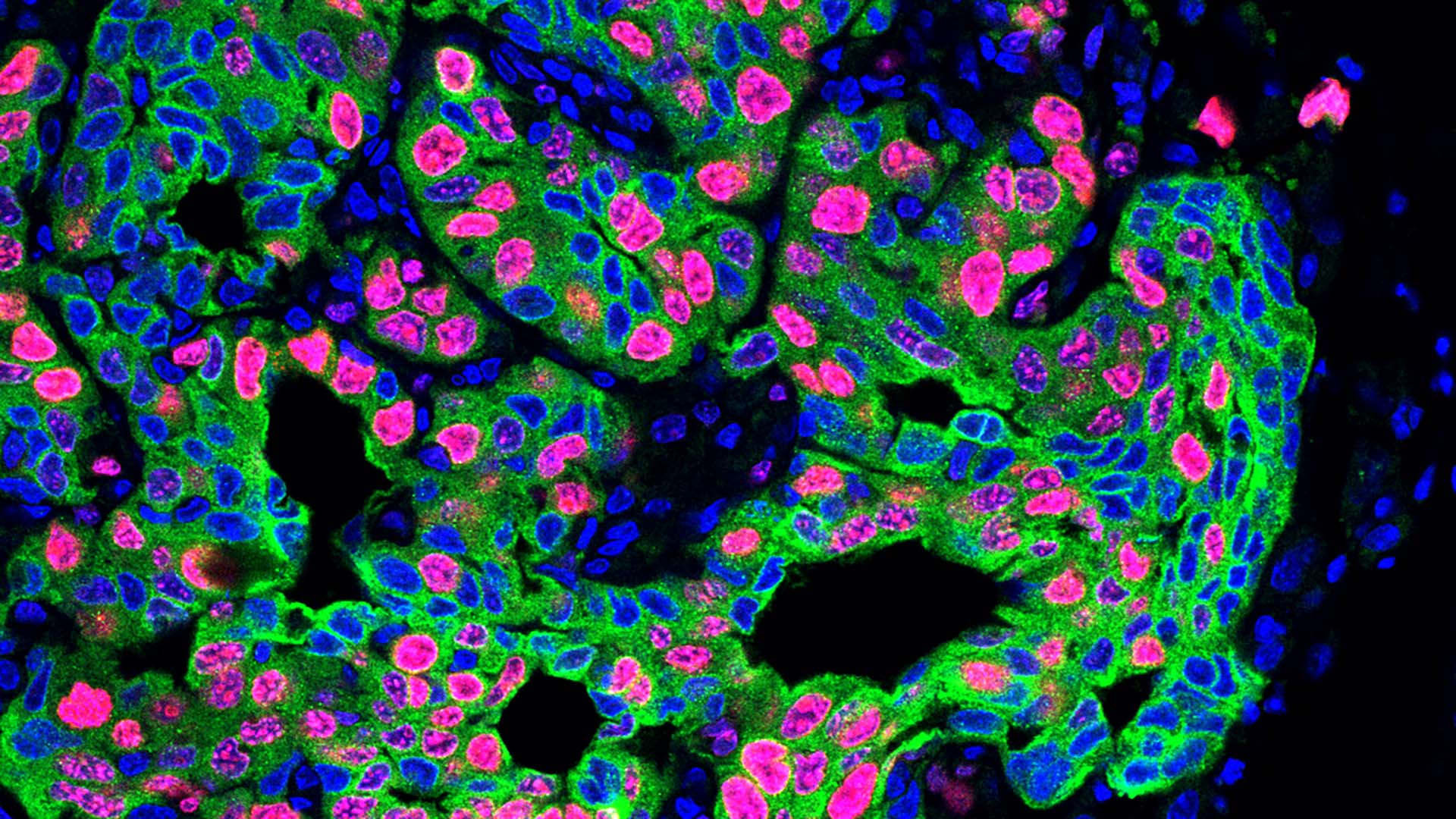
The team found that stress hormones called glucocorticoids acted on the neutrophils. These “stressed” neutrophils formed spider-web-like structures called NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps). NETs form when neutrophils expel DNA. Normally, they can defend us against invading microorganisms. However, in cancer, NETs create a metastasis-friendly environment.
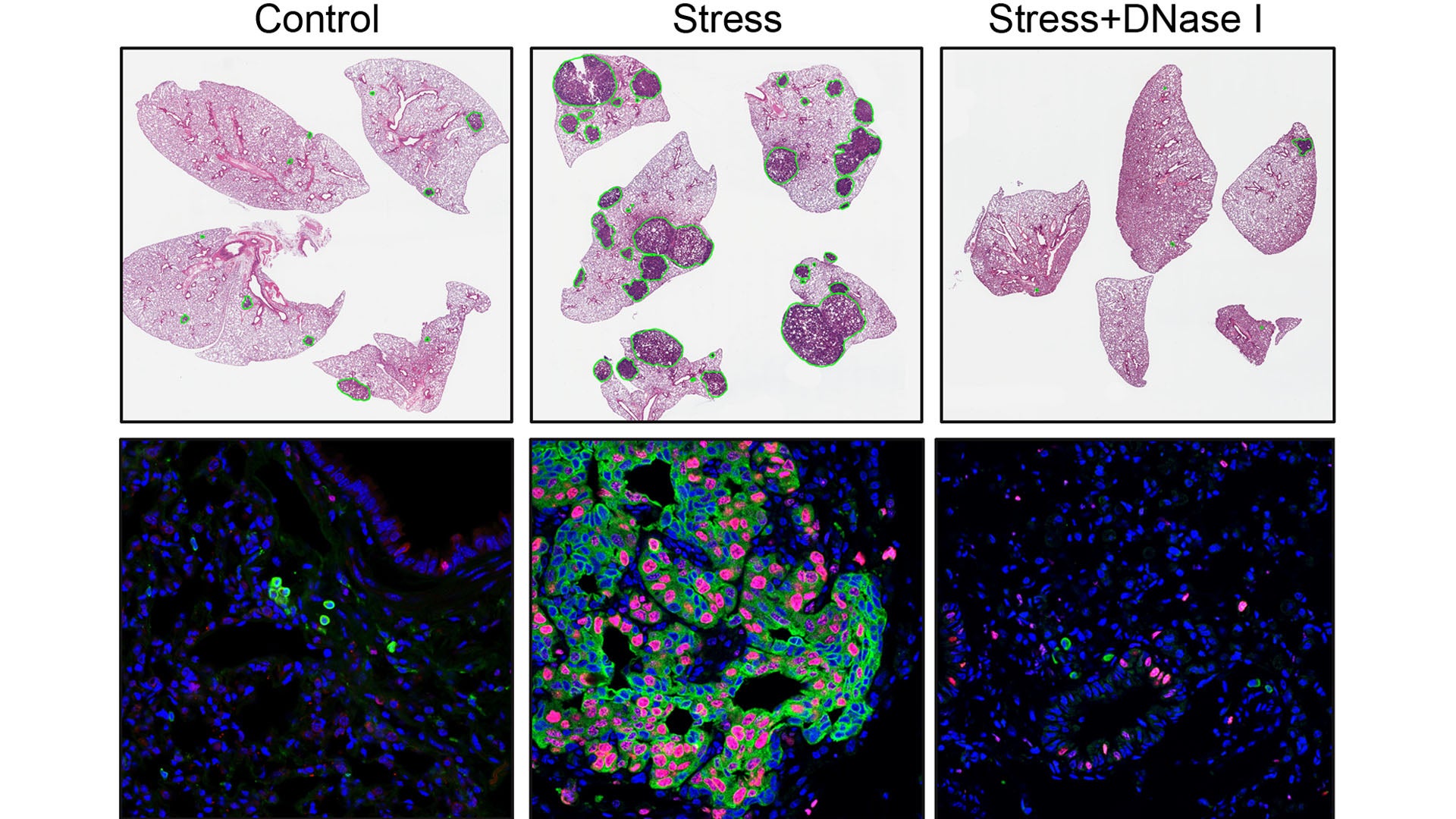
To confirm that stress triggers NET formation, leading to increased metastasis, He performed three tests. First, she removed neutrophils from the mice using antibodies. Next, she injected a NET-destroying drug into the animals. Lastly, she used mice whose neutrophils couldn’t respond to glucocorticoids. Each test achieved similar results. “The stressed mice no longer developed more metastasis,” He says.
Notably, the team found that chronic stress caused NET formation to modify lung tissue even in mice without cancer. “It’s almost preparing your tissue for getting cancer,” Egeblad explains.
To Van Aelst, the implication, though startling, is clear. “Reducing stress should be a component of cancer treatment and prevention,” she says.
The team also speculates that future drugs preventing NET formation could benefit patients whose cancer hasn’t yet metastasized. Such new treatments could slow or stop cancer’s spread, offering much-needed relief.
Written by: Margaret Osborne, Science Writer | [email protected] | 516-367-8455
Funding
National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program, American Association for Cancer Research, Cancer Research Institute, German Research Foundation
Citation
He, X. Y., et al., “Chronic stress increases metastasis via neutrophil-mediated changes to the microenvironment”, Cancer Cell, February 22, 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.01.013